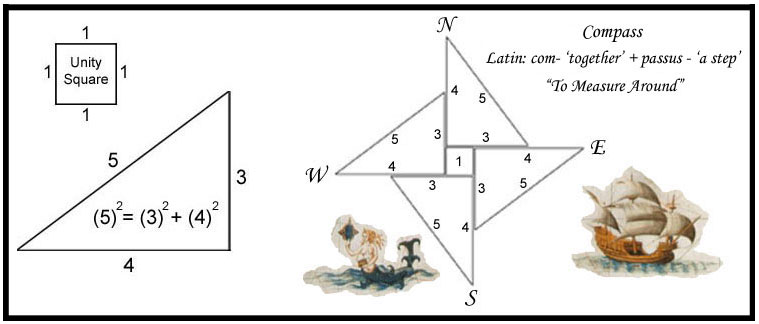
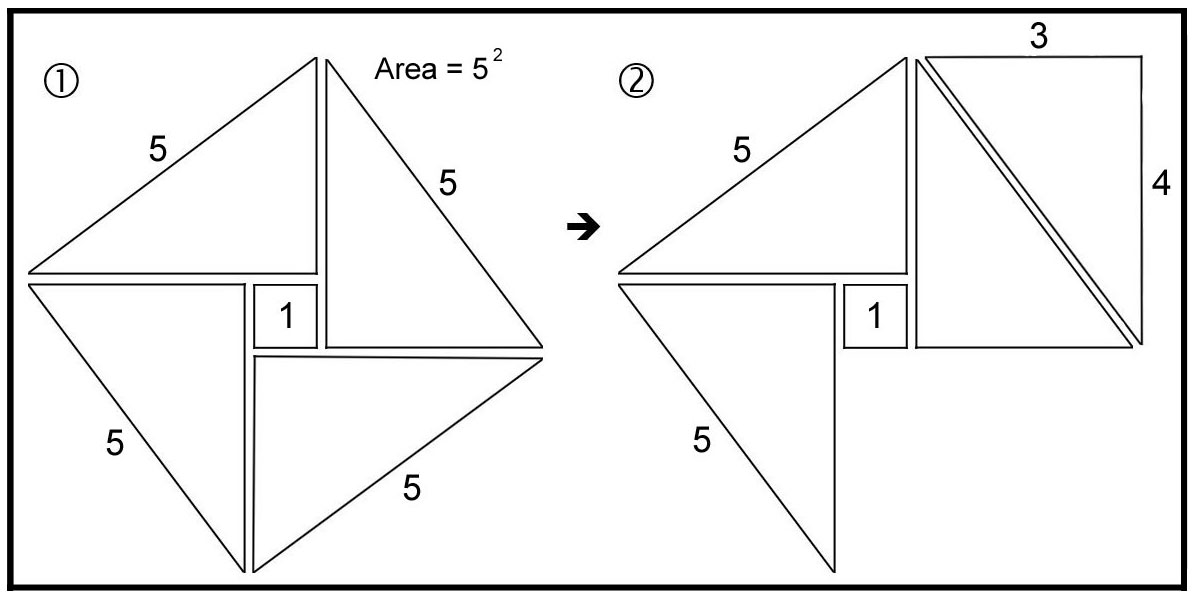
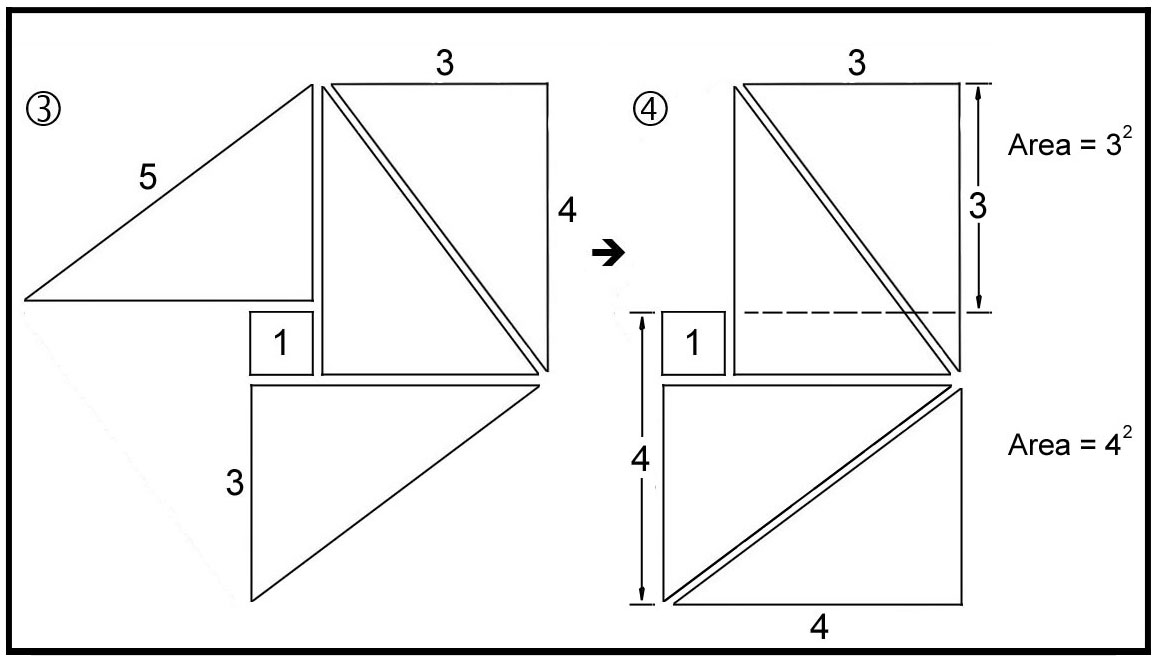
Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem can be understood visually using the ‘Unity Square’ and four ‘3-4-5’ Pythagorean triangles. You first start with a square of area of 25 (52). The goal is to rearrange the triangles so that we get two squares - one with and area of 9 (32) and the other with an area of 16 (42). The areas of (1) and (4) are the same – a visual proof of the Pythagorean Theorem.
|