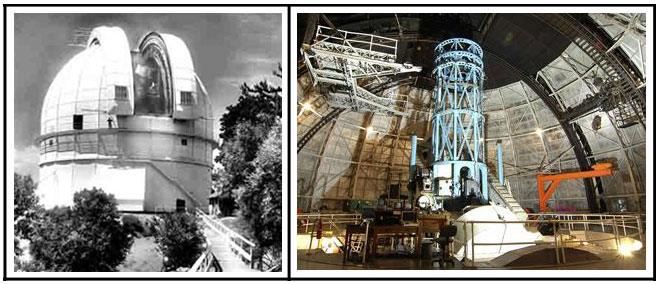
Hooker 100-inch Telescope The Saint-Gobain factory in France was selected to build the Hooker 100-inch lens, since it built the previous 60-inch lens for the Hale telescope (also on Mount Wilson). The blank was cast in 1906 and completed in 1908. The blank started with over two tons of fused glass which was melted in a furnace into one piece. It took over a year of cooling to prevent cracking. The telescope mounting mechanism incorporates a mercury float to provide smooth operation. The Hooker telescope saw “first light” on November 2, 1917. In 1919 an optical astronomical interferometer, developed by Albert Michelson, was installed to improve the precision of star diameter calculation (first time). In 1935 the silver coating was replaced with an improved aluminum metallic coating that reflected 50% more light. Hooker's reign of three decades as the largest telescope came to an end when the Caltech-Carnegie consortium completed its 200-inch Hale telescope in 1948 at Palomar Observatory, San Diego County, California.
|