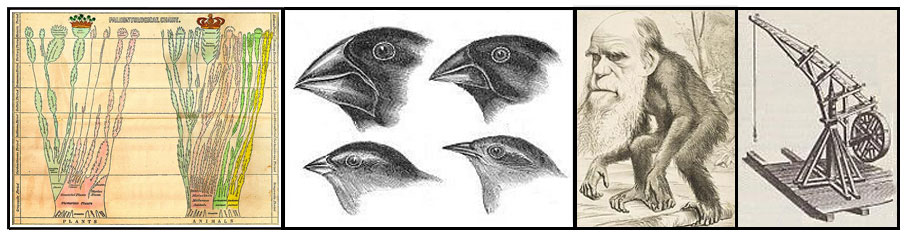
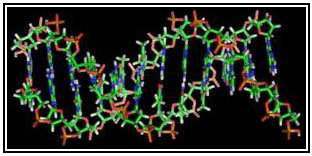
Genetics Timeline 1802 – Jean-Baptise Lamarack sets out hypothesis of inheritance of acquired characteristics 1859 – Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species, which sets out the theory of evolution by natural selection 1865 – Gregor Mendel presents his laws of inheritance to Natural History Society of Brunn 1869 – Friedrich Miescher discovers DNA, from pus-soaked bandages 1900 – Rediscovery of Mendel’s ideas by Hugo de Vries, Erich von Tschermak and Carl Correns 1910 – T.H. Morgan’s experiments with fruits flies show chromosomal basis of inheritance 1927 – Hermann Muller shows X-rays can cause genetic mutations 1941 – Geoge Beadle and Edward Tatum show that genes make proteins 1944 – Oswald Avery, Colin McLeod and Maclyn McCarty show DNA carries genetic information 1953 – Francis Crick and James Watson identify double-helix structure of DNA 1960 – Jacques Monod identifies role of messenger RNA in translating DNA into proteins 1961 – Marshall Nirenberg discovers first triplet DNA code for an amino acid 1975 – Fred Sanger develops chain-termination sequencing, the first efficient method of read genomes 1976 – Richard Dawkins publishes The Selfish Gene, which popularizes the gene-centered view of evolution 1981 – Martin
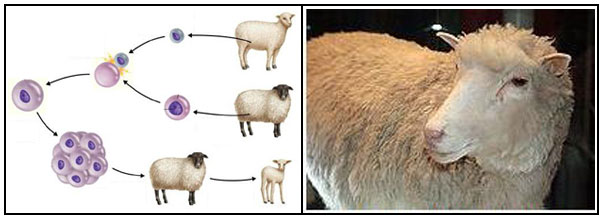
Evans isolated embryonic stem cells in mice 1985 – Creation of the first genetically modified crop, a tobacco strain 1989 – Creation of the first “knockout” mice, in wich genes have been switched off to investigate disease 1990 – Human Genome Project launched 1990 – First successful use of gene therapy to treat a human disease 1990 – Birth of Natalie and Danielle Edwards, the first babies screened as embryos to be free from a genetic disease 1993 – Discovery of Huntington’s disease mutation 1996 – Birth of Dolly the sheep, the first mammal cloned from an adult cell 1998 – Celera launches private effort to sequence the human genome 1998 – Jamie Thomson isolates human embryonic stem cells 2001 – Human Genome Project and Celera publish first drafts of humanity’s genetic code 2006 – Discovery of a new kind of genetic variation: widespread copy-number variation 2007 – Publication of first wave of genome-wide association studies, identifying common genes that contribute to common diseases, and launch of first direct-to-consumer genetic screening 2007 – Consortium shows that junk DNA and RNA are much more important to biology than had been thought
|